Auto-induction model
Auto-induction models have been proposed when the drug stimulates its own metabolism, usually via induction of the metabolic enzyme expression. Auto-induction models have for instance been used to describe the pharmacokinetics of Rifampin in Smythe et al. (2012), and of cyclophosphamide in Hassan et al. (1999).
The typical auto-induction model explicitly describes the enzyme level which is modeled using an turnover model with the drug inhibiting the enzyme degradation rate or increasing the enzyme production rate. The enzyme level is then taken into account in the apparent clearance for the drug.
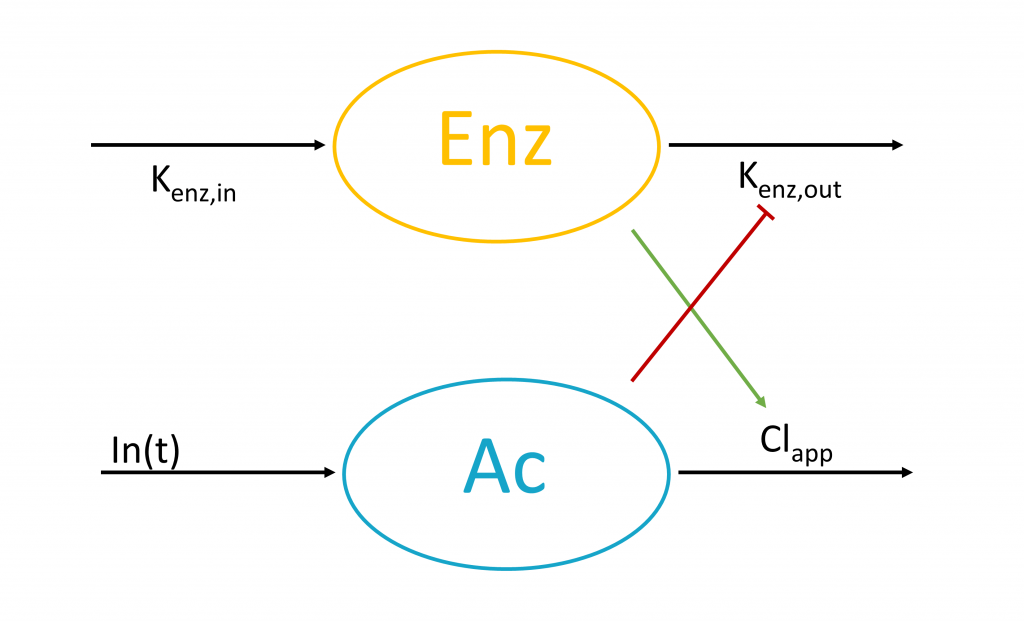
The typical equations read:
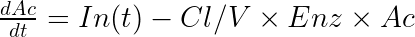
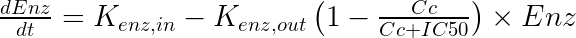
With In(t) the drug input rate. To avoid unidentifiability issues (i.e the product Cl*Enz0 is identifiable, but not Cl and Enz0 separately), the steady-state enzyme level is enforced to 1 which leads to ![]() . It is usually not necessary to introduce an Imax parameter.
. It is usually not necessary to introduce an Imax parameter.
Mlxtran code
For a zero-order absorption, the model reads:
[LONGITUDINAL]
input={Tk0, V, Cl, Kenz, IC50}
PK:
depot(target=Ac, Tk0)
EQUATION:
t_0 = 0
Ac_0 = 0
Enz_0 = 1
Cc = Ac/V
ddt_Ac = - Cl/V*Ac*Enz
ddt_Enz = Kenz - Kenz * (1- Cc/(Cc+IC50)) * Enz
OUTPUT:
output = {Cc}